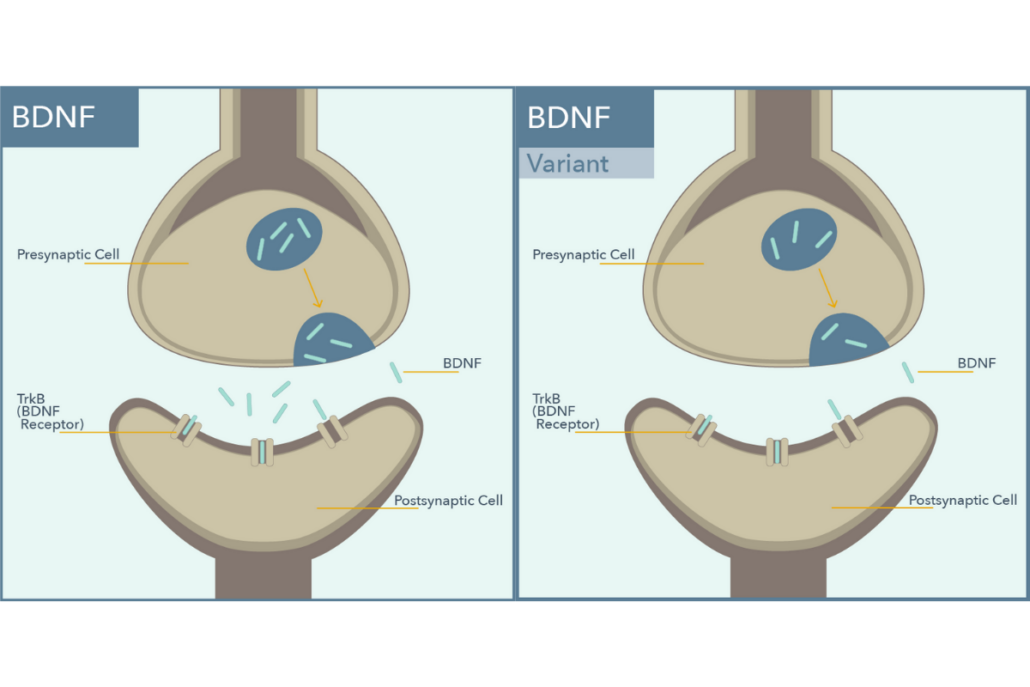
The Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) is a protein that regulates the growth, development and survival of neurons and promotes synaptic plasticity.1
Figure 1 demonstrates a fluoroscopic image of a rat retinal neuron that has been injected with BDNF and monitored for 48 hours. BDNF induces axonal growth/dendritic spine branching.2
Val66Met is a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the BDNF gene that is associated with reduced activity dependent secretion of BDNF.3 Met allele carriers of this BDNF genetic variant have been associated with increased risk of depression, memory impairment and altered stress response.4
Data from convergent research has helped scientists to postulate that physical activity improves cognition by modulating BDNF levels5. Specifically, a study of 1,032 subjects who underwent a battery of tests assessing memory showed that subjects with the Met allele of the BDNF gene (Val66Met) have greater improvement in working memory with exercise, compared to Val homozygotes.6 So, while exercise is beneficial for everyone, it may be most beneficial for Met allele carriers of BDNF, to improve working memory. A more recent study of U.S. military veterans supported the clinical utility of exercise as a means to address PTSD symptoms, dependent on BDNF genotype (Figure 2).
Adapted from Pitts BL, et al. BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and posttraumatic stress symptoms in U.S. military veterans: Protective effect of physical exercise. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019;100:198-202.
Figure 2 demonstrates results from a large study of European American U.S. military veterans with high lifetime trauma burden. BDNF Met allele carriers with high trauma burden reported greater severity of lifetime and past-month PTSD symptoms. Among veterans with high lifetime trauma burden, Met allele carriers who exercised had significantly lower severity of PTSD symptoms compared to those who did not exercise. 7
BDNF Val66Met polymorphism has also been shown to have different ethnicity-dependent associations with antidepressant response. Meta-analyses showed that Asian patients who are Met allele carriers have an increased odds of response to SSRIs compared to Val homozygotes.8,9 This is different from the antidepressant response seen in Caucasians (Figure 3).
Adapted from Colle R, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism and 6-month antidepressant remission in depressed Caucasian patients. J Affect Disord. 2015;175:233-240.
Figure 3 demonstrates results from a 6-month prospective study of 345 Caucasian patients with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD). At 3 months post-treatment, Met allele carriers of Val66Met had a higher probability of remission with SNRI/TCAs while those with Val/Val genotype were more likely to remit on SSRIs.10
This finding is consistent with data in previous animal studies but needs further replication in humans to confirm the clinical significance.
About one third of the population carries the Met allele of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism.5 Thus, genotype information for BDNF can be used to provide a more informed, personalized treatment regimen.6
Are You Ready to Upgrade Your Practice with Genomind?
Genomind’s pharmacogenetic testing is the most advanced and comprehensive mental health pharmacogenetic test available. Get access to 24 genes related to mental health, 130+ medications, 10+ conditions, state-of-the-art tools, and 360 degrees of support: register today.
References
- Notaras M, Hill R, van den Buuse M. The BDNF gene Val66Met polymorphism as a modifier of psychiatric disorder susceptibility: progress and controversy. Mol Psychiatry. 2015;20(8):916-930.
- Sanchez AL, Matthews BJ, Meynard MM, Hu B, Javed S, Cohen-Cory S. BDNF increases synapse density in dendrites of developing tectal neurons in vivo. Development. 2006;133:2477-2486.
- Martinez-Levy GA, Cruz-Fuentes CS. Genetic and epigenetic regulation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the central nervous system. Yale J Biol Med. 2014;87(2):173-186.
- Hosang GM SC, Tansey KE, McGuffin P, Uher R. Interaction between stress and the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2014;12(7).
- Nascimento CM, Pereira JR, Pires de Andrade L, Garuffi M, Ayan C, Kerr DS, et al. Physical exercise improves peripheral BDNF levels and cognitive functions in mild cognitive impairment elderly with different bdnf Val66Met genotypes. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;43(1):81-91.
- Erickson KI, Banducci SE, Weinstein AM, Macdonald AW, Ferrell RE, Halder I, et al. The brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism moderates an effect of physical activity on working memory performance. Psychol Sci. Sep 2013;24(9):1770-1779.
- Pitts BL, Whealin JM, Harpaz-Rotem I, Duman RS, Krystal JH, Southwick SM, et al. BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and posttraumatic stress symptoms in U.S. military veterans: Protective effect of physical exercise. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019;100:198-202.
- Niitsu T, Fabbri C, Bentini F, Serretti A. Pharmacogenetics in major depression: a comprehensive meta-analysis. Prog Neuropsycholopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013;45:183-194.
- Yan T, Wang L, Kuang W, Xu J, Li S. Chen J, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism association with antidepressant efficacy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asia Pac Psychiatry. 2014;6(3):241-251.
- Colle R, Gressier F, Verstuyft C, Deflesselle E, Lépine JP, Ferreri F, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism and 6-month antidepressant remission in depressed Caucasian patients. J Affect Disord. 2015;175:233-240.